TP53 and cancer
In normal, healthy cells, p53 is a tumor-suppressor protein that monitors for DNA damage and cellular stress, and that can prevent tumor progression.1,2 A mutation in the TP53 gene, which codes for the p53 protein, is commonly found in human cancers and can result in the loss or alteration of normal p53 protein function or a mutated p53 protein.3–6 Mutated p53 protein has an important role in cancer by altering cancer cell gene expression and thereby promoting tumor growth, survival, and progression.1,5,7–9
References: 1. Kastenhuber ER, et al. Cell. 2017;170:1062–1078; 2. Blagih J, et al. J Cell Sci. 2020;133:jcs237453; 3. Levine AJ. Ann Rev Cancer Biol. 2019;3:21–34; 4. Donehower LA, et al. Cell Rep. 2019;28:1370–1384.e1375; 5. Baugh EH, et al. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25:154–160; 6. Yue X, et al. J Mol Biol. 2017;429:1595–1606; 7. Alexandrova EM, et al. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8:e2661; 8. Mantovani F, et al. Cell Death Differ. 2019;26:199–212; 9. Roszkowska KA, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:1334.
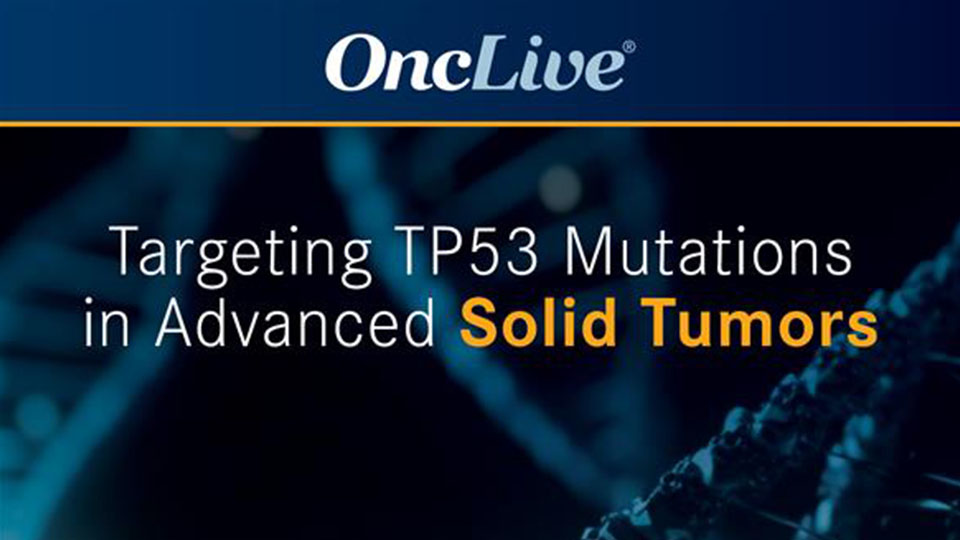
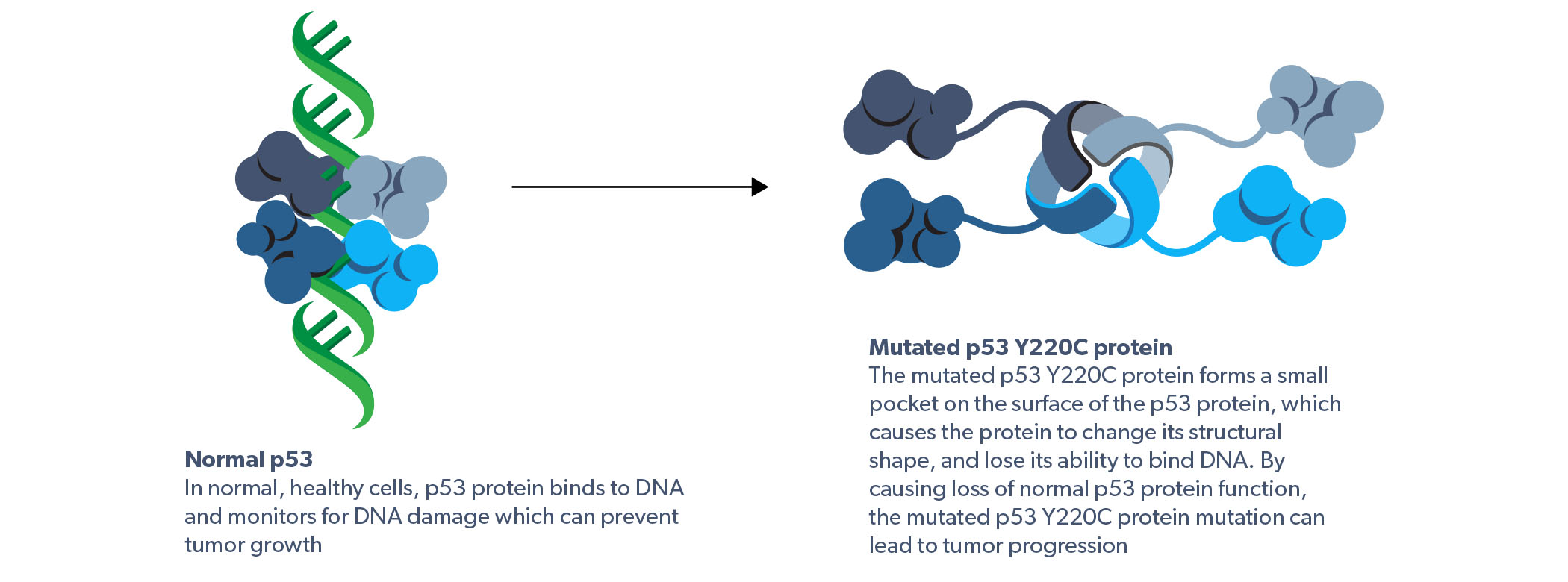
The TP53 Y220C mutation causes loss of normal p53 function
The mutated p53 Y220C protein forms a small pocket on the surface of p53 protein, which causes the protein to change its structural shape and lose its ability to bind DNA.1–6 By causing a loss of normal p53 protein function, the mutated p53 Y220C protein can lead to tumor progression and is therefore a potential therapeutic target in certain cancers.4–6
Impact of the TP53 Y220C mutation on the p53 protein
References: 1. Baugh EH, et al. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25:154–160; 2. Roszkowska KA, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:1334; 3. Bouaoun L, et al. Hum Mutat. 2016;37:865–876; 4. Blanden AR, et al. Drug Discov Today. 2015;20:1391–1397; 5. Baud MGJ, et al. Eur J Med Chem. 2018;152:101–114; 6. Tang Y, et al. J Phys Chem B. 2021;125:10138–10148.
The TP53 Y220C mutation is found
in many types of solid tumors
The TP53 Y220C mutation has been identified in over 30 different
solid tumor types.1,2 Across all solid tumors, ovarian cancer has
the highest frequency of TP53 Y220C mutations, followed by
endometrial cancer, breast cancer, and lung cancer.1 Biomarker
testing can identify genomic abnormalities in your patient's
tumor profile.3
Frequency of the TP53 Y220C mutation across common solid tumors
Ovarian (all)
2.8%
High-grade serous ovarian cancer
3.4%
Endometrial
1.1%
Breast
1.0%
Lung (all)
1.0%
Small cell lung cancer
1.6%
Non-small cell lung cancer
1.0%
References: 1. FoundationInsights™. A proprietary database used under license with review and approval from Foundation Medicine®. Available at: https://www.foundationmedicine.com/service/genomic-data-solutions. Accessed October 2025; 2. Schram A, et al. Poster presentation at AACR-NCI-EORTC 2023, Boston, USA. October 11–15, 2023; 3. American Cancer Society. Biomarker tests and cancer treatment. Available at: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/diagnosis-staging/tests/biomarker-tests.html. Accessed October 2025.
Rezatapopt is being investigated in TP53 Y220C cancer
Rezatapopt is a first-in-class, selective p53 reactivator specific to the mutated p53 Y220C protein.1–4 Rezatapopt is currently under investigation for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors that have a TP53 Y220C mutation (or TP53 Y220C cancer), including but not limited to ovarian cancer, lung cancer, breast cancer, and endometrial cancer.1–4
References: 1. ClinicalTrials. gov. NCT04585750. The evaluation of PC14586 in patients with advanced solid tumors harboring a p53 Y220C mutation. Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04585750. Accessed October 2025; 2. Dumble M, et al. Oral presentation at AACR 2021, Virtual. April 10–15, 2021; 3. Dumbrava EE, et al. Oral presentation at ASCO 2022, Chicago, USA. June 3–7, 2022; 4. Schram A, et al. Poster presentation at AACR-NCI-EORTC 2023, Boston, USA. October 11–15, 2023.
Resources
Further information on clinical studies
Your patient can learn more about clinical studies with the National Cancer Institute, American Cancer Society, and European Medicines Agency.
If your patient is interested in taking part in a clinical trial listed on clinicaltrials.gov, the Leal Health service can help them find the right trial, for free. Share this link with your patient to provide them with more information.
To learn more about rezatapopt in the PYNNACLE study, please visit clinicaltrials.gov.
Please contact the PMV Pharmaceuticals Clinical Study Information Center
+1 (609) 235-4038
clinicaltrials@pmvpharma.com
Rezatapopt is an investigational agent that has not been approved by any health authority.
Images do not depict actual trial participants.
MA-586-0107 October 2025